24-hour hotline:+8613662168047
Keyword search: battery plant , lithium battery factory , power bank works , lifepo4 battery mill , lithium forklift battery manufacturer
Lithium batteries are a type of battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as the negative electrode material and non-aqueous electrolyte solutions. In 1912, lithium-metal batteries were first developed by Gilbert N Lewis proposed and studied. In the 1970s, M S. Whittingham proposed and began researching lithium-ion batteries. Due to the highly reactive chemical properties of lithium metal, the processing, storage, and use of lithium metal have very high environmental requirements. So, lithium batteries have not been applied for a long time. With the development of science and technology, lithium batteries have become mainstream now.
Lithium batteries can be roughly divided into two categories: lithium metal batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Lithium ion batteries do not contain metallic lithium and are rechargeable. The fifth generation product of rechargeable batteries, lithium metal batteries, was born in 1996. Their safety, specific capacity, self discharge rate, and cost-effectiveness are all superior to lithium-ion batteries. Due to its own high-tech requirements, only a few companies from different countries are currently producing this type of lithium metal battery.
Battery life
Can lithium-ion batteries only be charged and discharged 500 times?
I believe the vast majority of consumers have heard that the lifespan of lithium batteries is "500 times". After 500 charges and discharges, the battery will "end its life". Many friends, in order to extend the battery's lifespan, charge it every time the battery is completely depleted. Does this really have an effect on extending the battery's lifespan? The answer is negative. The lifespan of a lithium battery is 500 cycles, which refers not to the number of charges, but to one cycle of charging and discharging.
A charging cycle means the process of all the battery's charge going from full to empty, and then from empty to full, which is not equivalent to charging once. For example, a lithium battery only uses half of its capacity on the first day and then fully charges it. If it continues like this the next day, charging half of it and charging it twice in total, this can only be counted as one charging cycle, not two. Therefore, it may usually take several charges to complete a cycle. Every time a charging cycle is completed, the battery capacity will decrease slightly. However, the reduction in battery capacity is very small. After multiple cycles of charging, high-quality batteries still retain 80% of their original capacity. Many lithium-ion powered products are still used as usual after two to three years. Of course, lithium batteries still need to be replaced at the end of their lifespan.
The so-called 500 times refers to the manufacturer achieving about 625 rechargeable times at a constant discharge depth (such as 80%), reaching 500 charging cycles.
(80% * 625=500) (ignoring factors such as reduced lithium battery capacity)
Due to various impacts in practical life, especially the discharge depth during charging is not constant, "500 charging cycles" can only be used as a reference for battery life.
Source: JUDA LARGE2018-05-08 Click through: 311
In 1746, Mason Brock from Leiden University in the Netherlands invented the Leiden bottle for collecting charges. Because he saw that the electricity he had finally collected was easily disappearing into the air, he wanted to find a way to preserve it. One day, he suspended a gun barrel in the air, connected it to the motor, and inserted a copper wire from the barrel into a glass bottle filled with water. He had an assistant hold the glass bottle with one hand, and Mason Brock vigorously shook the motor on the side. At this moment, his assistant accidentally hit the other hand with the barrel of the gun, and he suddenly felt a strong electric shock and shouted. Mason Brock then swapped with his assistant and had them shake the motor. He held the water bottle with one hand and touched the barrel with the other.
In 1780, Italian anatomist Luigi Galvani, while dissecting a frog, accidentally touched the frog's thigh with different metal instruments in his hands. The frog's leg muscles immediately twitched, as if stimulated by an electric current. If only one metal instrument was used to touch the frog, there would be no such reaction. Gavanni believed that this phenomenon occurred due to a type of electricity generated within the animal body, which he called "bioelectricity.".
The discovery of Gavanni aroused great interest among physicists, who competed to repeat Gavanni's experiments in an attempt to find a way to generate electricity. Italian physicist Volt believed after multiple experiments that Gavanni's theory of "bioelectricity" was not correct. The reason why frog muscle can generate electricity is probably because a certain liquid in the muscle is working. To argue his point, Volt immersed two different metal plates in various solutions for experimentation. It was found that as long as one of these two metal sheets undergoes a chemical reaction with the solution, an electric current can be generated between the metal sheets.
In 1799, Italian physicist Volt immersed a zinc plate and a tin plate in salt water and discovered that there was an electric current flowing through the wire connecting the two metals. So, he placed many zinc and silver sheets between them, soaked in saltwater, and stacked them flat. When touching both ends with your hands, you will feel strong electrical stimulation. Volt successfully produced the world's first battery using this method - the Volt stack. This "volt stack" is actually a series of battery packs. It became an early electrical experiment, where the electricity from the telegraph machine came from a battery source.
In 1836, Daniel from England made improvements to the "volt stack". He used dilute sulfuric acid as the electrolyte to solve the polarization problem of the battery and created the first zinc copper battery that was not polarized and could maintain a balanced current. Since then, these batteries have had the problem of voltage decreasing with prolonged use.
When the voltage of the battery drops after a period of use, reverse current can be applied to it, causing the battery voltage to rise. Because this type of battery can be charged and reused, it is called a "battery".
In 1860, George Leclanche of France also invented the predecessor of the widely used battery (carbon zinc battery) worldwide. Its negative electrode is an alloy rod of zinc and mercury (the negative electrode of a zinc volt prototype battery, which has been proven to be one of the best metal materials for negative electrode production), and its positive electrode is a porous cup containing a mixture of crushed manganese dioxide and carbon. A carbon rod is inserted into this mixture as a current collector. The negative electrode rod and positive electrode cup are both immersed in ammonium chloride solution as the electrolyte. This system is called a "wet battery". The batteries manufactured by Lexus were simple but cheap, so they were not replaced by improved "dry batteries" until 1880. The negative electrode is improved into a zinc tank (i.e. the outer shell of the battery), and the electrolyte becomes a paste instead of a liquid, which is basically what we are familiar with as a carbon zinc battery.
In 1887, Englishman Helen invented the earliest dry battery. The electrolyte of dry batteries is paste like and will not leak, making it easy to carry and therefore widely used.
In 1890, Thomas Edison invented the rechargeable nickel iron battery.
A battery refers to a portion of the space in a cup, tank, or other container or composite container that contains an electrolyte solution and metal electrodes to generate electricity, and a device that can convert chemical energy into electrical energy. It can be divided into positive and negative electrodes. With the advancement of technology, batteries generally refer to small devices that can generate electricity. Like solar cells. The performance parameters of batteries mainly include electromotive force, capacity, specific energy, and resistance. By using batteries as an energy source, stable voltage, stable current, long-term stable power supply, and minimal external influence can be obtained. The battery structure is simple, easy to carry, and the charging and discharging operations are simple and easy to operate. It is not affected by external climate and temperature, and its performance is stable and reliable. It has played a significant role in various aspects of modern social life.
The service life of lithium batteries is only two to three years.
Lithium batteries can generally be charged and discharged 300-500 times. It is best to partially discharge lithium batteries instead of completely discharging them, and to avoid frequent complete discharge as much as possible. Once the battery is taken off the production line, the clock starts to move. Regardless of whether you use it or not, the lifespan of lithium batteries is only two to three years.
Lithium batteries are a type of battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as the negative electrode material and non-aqueous electrolyte solutions. In 1912, lithium-metal batteries were first developed by Gilbert N Lewis proposed and studied. In the 1970s, M S. Whittingham proposed and began researching lithium-ion batteries. Due to the highly reactive chemical properties of lithium metal, the processing, storage, and use of lithium metal have very high environmental requirements. So, lithium batteries have not been applied for a long time. With the development of science and technology, lithium batteries have become mainstream now.
Lithium batteries can be roughly divided into two categories: lithium metal batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Lithium ion batteries do not contain metallic lithium and are rechargeable. The fifth generation product of rechargeable batteries, lithium metal batteries, was born in 1996. Their safety, specific capacity, self discharge rate, and cost-effectiveness are all superior to lithium-ion batteries. Due to its own high-tech requirements, only a few companies from different countries are currently producing this type of lithium metal battery.
1. The shelf life refers to the period of time from the production of a product to the general occurrence of quality problems, and it is also possible that some product quality will remain in a normal state after this period, so it has uncertainty. The buyer is passive during the shelf life.
2. Validity period refers to certain items (things) that can be used or done within a certain period of time, with clear time limits. The user has the initiative during the validity period.
3. Generally, batteries are printed with their expiration date instead of the factory date, and the approximate manufacturing time should be calculated from the expiration date. For example, "02-01" has an expiration date of February 2001. Generally,:
(1) The shelf life of alkaline batteries is 3 years;
(2) The shelf life of P-type batteries is 2 years;
(3) The shelf life of ordinary batteries is 1 year;
(4) Foreign brands have a printing shelf life of 1-2 years longer than domestic brands, so different types of batteries mentioned above should be added

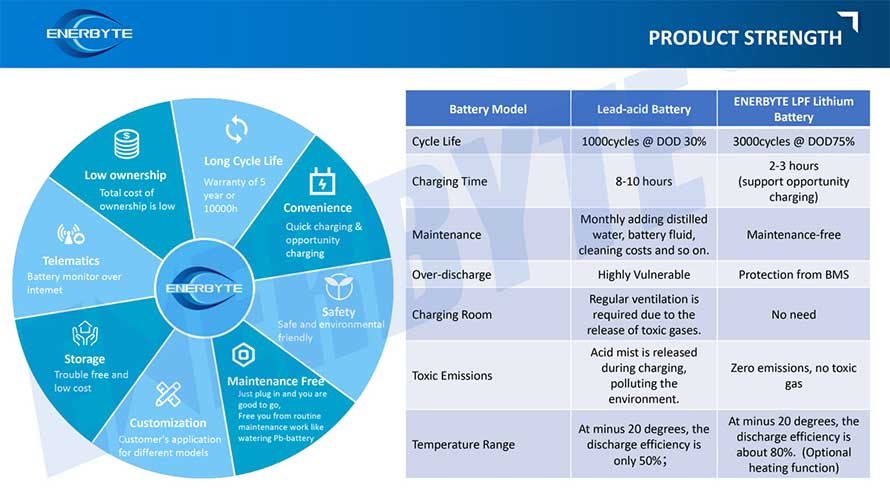
Lithium ForkLift Batteries ,Ensure Quality
Our lithium battery production line has a complete and scientific quality management system
Ensure the product quality of lithium batteries

Years of experience in producing lithium forklift batteries
Focus on the production of lithium batteries

WE PROMISE TO MAKE EVERY LITHIUM BATTERY WELL
We have a comprehensive explanation of lithium batteries

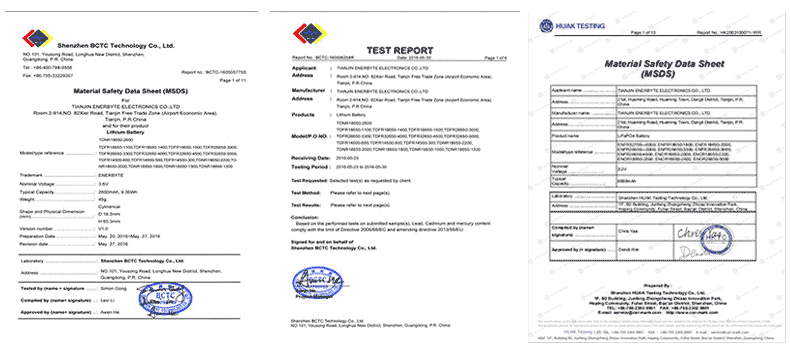
QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATE
THE QUALITY OF COMPLIANCE PROVIDES GUARANTEE FOR CUSTOMERS
MULTIPLE QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATES TO ENSURE STABLE PRODUCT QUALITY
Providing customers with professional and assured products is the guarantee of our continuous progress.


Applicable brands of our products

| Linde Lithium Forklift Battery | Toyota Lithium Forklift Battery | hyster Lithium Forklift Battery |
| jung Lithium Forklift Battery | enrich Lithium Forklift Battery | hyundai Lithium Forklift Battery |
| still Lithium Forklift Battery | heli Lithium Forklift Battery | hangcha Lithium Forklift Battery |

 Service hotline
Service hotline