24-hour hotline:+8613662168047
Keyword search: battery plant , lithium battery factory , power bank works , lifepo4 battery mill , lithium forklift battery manufacturer
Lithium battery is divided into lithium ion battery and lithium ion battery. At present, mobile phones and laptops use lithium-ion batteries, commonly known as lithium-ion batteries. This article will discuss the lithium-ion batteries currently used in mobile phones, etc., but the real lithium-ion batteries are not used in daily electronic products because of their high risk.
Lithium-ion batteries use carbon materials as the negative electrode and compounds containing lithium as the positive electrode. There is no metal lithium, but only lithium ion. This is the lithium-ion battery. Lithium ion battery refers to the general term of battery with lithium ion intercalation compound as cathode material. The charge and discharge process of lithium ion battery is the process of lithium ion insertion and removal. In the process of lithium ion insertion and de-insertion, there is also the insertion and de-insertion of equivalent electrons with lithium ion (traditionally, the positive electrode is represented by insertion or de-insertion, while the negative electrode is represented by insertion or de-insertion). In the process of charging and discharging, lithium ions are inserted/removed and inserted/removed back and forth between the positive and negative electrodes, which is vividly referred to as the rocking chair battery.
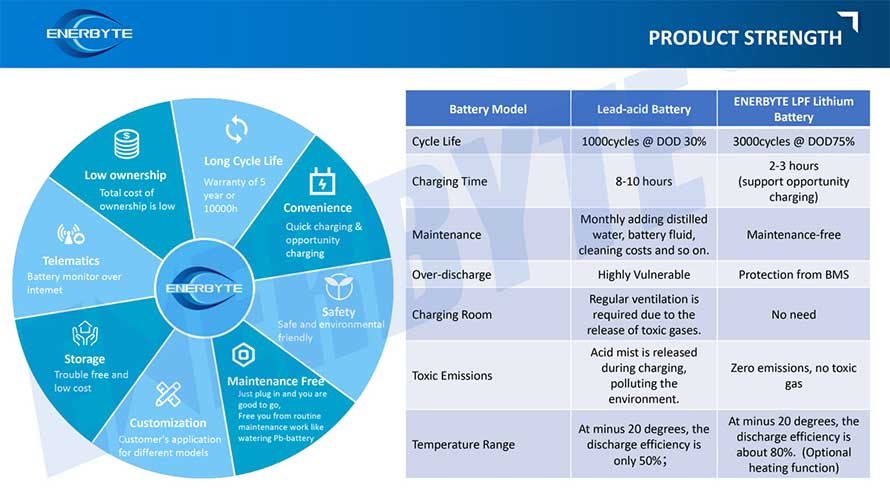
Lithium ion battery has high energy density and uniform output voltage. Self-discharge is small, less than 10% per month. There is no memory effect. The operating temperature range is - 20 ℃~60 ℃. Excellent cycle performance, fast charging and discharging, charging efficiency up to 100%, and large output power. Long service life. Without environmental pollution, it is called green battery.
Charging is a critical step in battery reuse. The charging process of lithium-ion batteries is divided into two stages: constant current fast charging stage (the indicator light is red or yellow) and constant voltage current decreasing stage (the indicator light is green). At the constant current fast charging stage, the battery voltage gradually rises to the standard voltage of the battery, and then moves to the constant voltage stage under the control chip. The voltage does not rise to ensure that it will not overcharge, and the current gradually decreases to 0 with the increase of the battery power, and finally completes the charging. The power statistics chip can sample and calculate the battery power by recording the discharge curve. The discharge curve of lithium-ion battery will change after many times of use. Although there is no memory effect in lithium-ion battery, improper charging will seriously affect the battery performance.
Excessive charging and discharging of lithium-ion batteries will cause permanent damage to the positive and negative electrodes. Excessive discharge leads to the collapse of the carbon layer structure of the negative electrode, and the collapse will cause the lithium ion cannot be inserted during the charging process; Over-charging causes too many lithium ions to be embedded in the carbon structure of the negative electrode, and some of them can no longer be released.
The charging amount is equal to the charging current times the charging time. When the charging control voltage is fixed, the higher the charging current (the faster the charging speed), the lower the charging charge. The battery charging speed is too fast and the termination voltage control point is improper, which will also cause the battery capacity to be insufficient. In fact, some of the electrode active substances of the battery will stop charging without sufficient reaction. This phenomenon of insufficient charging will intensify with the increase of the number of cycles.
hidden danger
The safety of lithium-ion battery is not only related to the nature of the cell material itself, but also related to the battery preparation technology and use. Mobile phone batteries frequently explode, on the one hand, because of the failure of the protective circuit, but more importantly, there is no fundamental treatment problem in terms of materials.
Lithium cobaltate positive active material is a very mature system in terms of small cells, but after overflowing, there are still a large number of lithium ions left in the positive pole. When overcharged, the lithium ions left in the positive pole will rush to the negative pole. The formation of dendrites on the negative pole is the inevitable result of overcharge of batteries using lithium cobaltate material. Even in the normal charging and discharging process, there may be excess lithium ions dissociated to the negative pole to form dendrites, The theoretical specific energy of lithium cobaltate is more than 270 mAh per gram, but to ensure its cycle performance, the actual capacity used is only half of the theoretical capacity. In the process of use, if the battery charging voltage is too high due to some reason (such as the damage of the management system), the remaining lithium in the positive electrode will be removed, and the dendrite will be deposited in the form of metallic lithium on the surface of the negative electrode through the electrolyte. Dendrites pierce the diaphragm and form internal short circuit.
The critical component of the electrolyte is carbonate, which has a low flash point and low boiling point, and will burn or even explode under certain conditions. If the battery overheats, the carbonate in the electrolyte will be oxidized and reduced, and a large amount of gas and more heat will appear. If there is no safety valve or the gas cannot be released through the safety valve in time, the internal pressure of the battery will rise sharply and cause explosion.
The polymer electrolyte lithium-ion battery does not fundamentally deal with the safety problem. The lithium cobaltate and organic electrolyte are also used, and the electrolyte is colloidal and not easy to leak, which will cause more severe combustion. Combustion is the biggest safety problem of polymer battery.
There are also some problems in the use of the battery. In case of external short circuit or internal short circuit, there will be hundreds of amperes of excessive current. In case of external short circuit, the battery will discharge with large current instantaneously, which will consume a lot of energy on the internal resistance and generate huge heat. The internal short circuit forms a large current, the temperature rise causes the diaphragm to melt, and the short circuit area expands, thus forming a vicious circle.
In order to reach the high working voltage of 3~4.2V for a single cell, the lithium-ion battery has to use organic electrolyte with an analytical voltage greater than 2V. However, the organic electrolyte will be electrolyzed under high current and high temperature conditions, and gas will appear in the electrolysis, which will lead to the increase of internal pressure and serious breakthrough of the shell.
Over-charging may precipitate metal lithium, and when the shell is broken, it will be in direct contact with the air, resulting in combustion. At the same time, it will ignite the electrolyte, causing a strong flame, rapid expansion of the gas, and explosion.
In addition, due to improper use of lithium-ion batteries for mobile phones, such as extrusion, impact and water ingress, the battery will expand, deform and crack, which will lead to short circuit of the battery and cause explosion due to heat release during discharge or charging.
Safety design
In order to prevent the battery from discharging or overcharging due to improper use, a triple protection mechanism is set in the single lithium-ion battery. One is the use of switching elements. When the temperature in the battery rises, its resistance will rise. When the temperature is too high, it will automatically stop power supply; The second is to select appropriate partition materials. When the temperature rises to a certain value, the micro-pores on the partition will be dissolved automatically, so that lithium ion cannot pass through and the internal reaction of the battery stops; The third is to set the safety valve (the vent hole on the top of the battery). When the internal pressure of the battery rises to a certain value, the safety valve will automatically open to ensure the safety of the battery.
Sometimes, although the battery itself has safety control measures, the internal pressure of the battery will rise sharply and cause explosion because of the control failure caused by some reasons, the lack of safety valve or the lack of time to release the gas through the safety valve.
In general, the total energy stored by lithium-ion batteries is inversely proportional to their safety. With the increase of battery capacity, the battery volume is also increasing, its heat dissipation performance becomes poor, and the possibility of accidents will increase significantly. For lithium-ion batteries for mobile phones, the basic requirements are
The probability of safety accidents is less than one in a million, which is also the lowest standard accepted by the public. It is particularly important to use forced cooling for large-capacity lithium-ion batteries, especially for automobiles.
The selection of safer electrode material and lithium manganate material ensures that the molecular structure is fully charged. The lithium ion of the positive electrode has been completely embedded in the carbon hole of the negative electrode, fundamentally preventing the appearance of dendrites. At the same time, the stable structure of lithium manganate makes its oxidation performance far lower than that of lithium cobaltate. The analysis temperature is more than 100 ℃ of lithium cobaltate. Even if internal short circuit (acupuncture), external short circuit and overcharge occur due to external force, it can completely guard against the danger of combustion and explosion caused by the precipitation of lithium metal.
In addition, the use of lithium manganate material can also significantly reduce costs.
To improve the performance of the existing safety control technology, the first step is to improve the safety performance of lithium-ion battery cells, which is particularly important for large-capacity batteries. Select a diaphragm with good thermal sealing performance. The purpose of the diaphragm is to allow the passage of lithium ion while isolating the positive and negative poles of the battery. When the temperature rises, the diaphragm is sealed before melting, so that the internal resistance rises to 2000 ohms and the internal reaction stops.
When the internal pressure or temperature reaches the preset standard, the explosion-proof valve will open and begin to relieve pressure to prevent excessive accumulation of internal gas and deformation, which will eventually lead to the shell bursting.
Improve control dexterity, select more dexterous control parameters and adopt joint control of multiple parameters (this is particularly important for large capacity batteries). The large capacity lithium-ion battery pack is composed of multiple cells in series/parallel, such as
The voltage of notebook computer is more than 10V, and the capacity is large. Generally, 3~4 single batteries in series can meet the voltage requirements, and then 2~3 battery packs in series are connected in parallel to ensure a large capacity.
The large-capacity battery pack itself must be equipped with relatively complete protection functions, and two kinds of circuit board modules should also be considered: the protection board PCb module and the Smartbattery Gaugeboard module. The complete battery protection design includes: Level 1 protection IC (against overcharge, over-discharge and short circuit of battery), Level 2 protection IC (against the second overvoltage), fuse, LED indication, temperature regulation and other components.

Lithium ForkLift Batteries ,Ensure Quality
Our lithium battery production line has a complete and scientific quality management system
Ensure the product quality of lithium batteries

Years of experience in producing lithium forklift batteries
Focus on the production of lithium batteries

WE PROMISE TO MAKE EVERY LITHIUM BATTERY WELL
We have a comprehensive explanation of lithium batteries

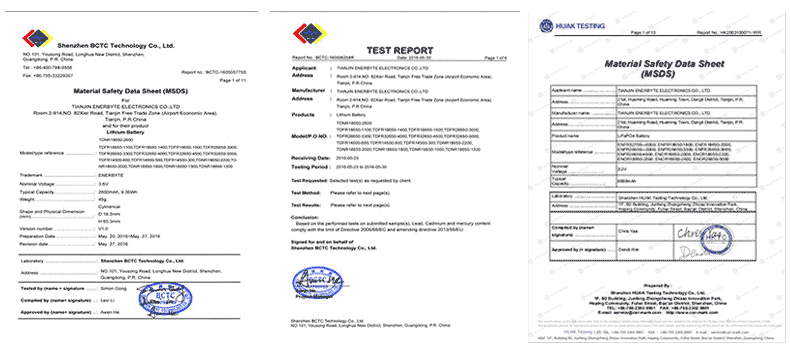
QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATE
THE QUALITY OF COMPLIANCE PROVIDES GUARANTEE FOR CUSTOMERS
MULTIPLE QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATES TO ENSURE STABLE PRODUCT QUALITY
Providing customers with professional and assured products is the guarantee of our continuous progress.


Applicable brands of our products

| Linde Lithium Forklift Battery | Toyota Lithium Forklift Battery | hyster Lithium Forklift Battery |
| jung Lithium Forklift Battery | enrich Lithium Forklift Battery | hyundai Lithium Forklift Battery |
| still Lithium Forklift Battery | heli Lithium Forklift Battery | hangcha Lithium Forklift Battery |

 Service hotline
Service hotline