24-hour hotline:+8613662168047
Keyword search: battery plant , lithium battery factory , power bank works , lifepo4 battery mill , lithium forklift battery manufacturer
A battery is an electrochemical device that stores chemical energy and releases electrical energy when necessary. It uses a lead substrate grid filled with sponge like lead (also known as a grid) as the negative electrode, a lead substrate grid filled with lead dioxide as the positive electrode, and dilute sulfuric acid with a density of 1.26-1.33g/mlg/ml as the electrolyte. When the battery is discharged, the metal lead is the negative electrode, which undergoes an oxidation reaction and generates lead sulfate; Lead dioxide is a positive electrode that undergoes a reduction reaction to produce lead sulfate. When the battery is charged with direct current, the two poles generate elemental lead and lead dioxide, respectively. After removing the power supply, it returns to its pre discharge state and forms a chemical battery. A battery can be repeatedly charged and discharged, and its individual voltage is 2V. A battery is a battery pack composed of one or more individual cells, abbreviated as a battery. The most common type is 6V, and other types of batteries include 2V, 4V, 8V, and 24V. For example, the battery used in cars (commonly known as a battery) is a 12V battery pack consisting of six batteries connected in series. Regarding traditional dry load batteries (such as automotive and motorcycle dry load batteries), distilled water should be added after a period of use to maintain a density of about 1.28g/ml of dilute sulfuric acid electrolyte; Regarding maintenance free batteries, distilled water is no longer required until the end of their lifespan. According to a survey conducted by the editor of Optics Valley at Jiaotong University on conventional battery manufacturers in the market, it is understood that:
There are different methods for classifying batteries, which can be generally divided into three categories. The first category includes alkaline batteries, batteries with potassium hydroxide as the main electrolyte, such as alkaline zinc manganese batteries (commonly known as alkaline manganese batteries or alkaline batteries), cadmium nickel batteries, nickel hydrogen batteries, etc. Acid batteries, mainly using sulfuric acid aqueous solution as the medium, such as zinc manganese dry batteries (also known as acid batteries by some consumers), seawater batteries, etc; Organic electrolyte batteries are important batteries that use organic solutions as the medium, such as lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion batteries, etc. Type 2: Classified by nature of work and storage method, it includes: primary batteries, also known as primary batteries, i.e. batteries that cannot be recharged, such as zinc manganese dry batteries, lithium primary batteries, etc; Secondary batteries, such as nickel hydrogen batteries, lithium-ion batteries, cadmium nickel batteries, etc; Traditionally, batteries refer to lead-acid batteries, which are also secondary batteries; Fuel power cells, where active materials are continuously added to the battery from the outside during operation, such as hydrogen oxygen fuel power cells; Reserve batteries, that is, batteries are stored without direct contact with the electrolyte until they are in use before adding the electrolyte, such as silver magnesium batteries, also known as seawater batteries. The third category: divided by the positive and negative electrode materials used in batteries, including: zinc series batteries, such as zinc manganese batteries, zinc silver batteries, etc; Nickel series batteries, such as cadmium nickel batteries, hydrogen nickel batteries, etc.: lead series batteries, such as lead-acid batteries, etc; Lithium ion batteries, lithium manganese batteries; Manganese dioxide series batteries, such as zinc manganese batteries, alkaline manganese batteries, etc; Air (oxygen) series batteries, such as zinc air batteries.
1. There are several important types of lead-acid battery products, and their usage distribution is as follows:
Starting type batteries: important for starting and lighting in automobiles, motorcycles, tractors, diesel engines, etc;

Lithium ForkLift Batteries ,Ensure Quality
Our lithium battery production line has a complete and scientific quality management system
Ensure the product quality of lithium batteries

Years of experience in producing lithium forklift batteries
Focus on the production of lithium batteries

WE PROMISE TO MAKE EVERY LITHIUM BATTERY WELL
We have a comprehensive explanation of lithium batteries

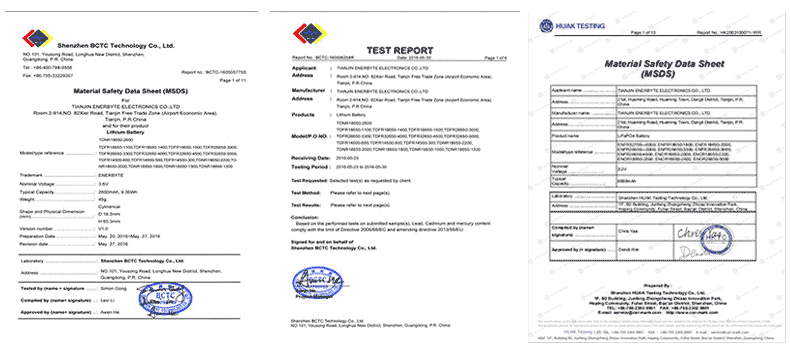
QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATE
THE QUALITY OF COMPLIANCE PROVIDES GUARANTEE FOR CUSTOMERS
MULTIPLE QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATES TO ENSURE STABLE PRODUCT QUALITY
Providing customers with professional and assured products is the guarantee of our continuous progress.


Applicable brands of our products

| Linde Lithium Forklift Battery | Toyota Lithium Forklift Battery | hyster Lithium Forklift Battery |
| jung Lithium Forklift Battery | enrich Lithium Forklift Battery | hyundai Lithium Forklift Battery |
| still Lithium Forklift Battery | heli Lithium Forklift Battery | hangcha Lithium Forklift Battery |

 Service hotline
Service hotline