24-hour hotline:+8613662168047
Keyword search: battery plant , lithium battery factory , power bank works , lifepo4 battery mill , lithium forklift battery manufacturer
Principle of spontaneous combustion
Lithium is the most active metal in the world. The small size, high capacity density, and high energy density of lithium-ion batteries make them the preferred choice for electric vehicles. Lithium ion batteries utilize the gain and loss of electrons and migration aggregation of lithium ions to store electrical energy during operation.
When charging a battery, the lithium atoms in the positive electrode will lose electrons and become lithium ions, creating a potential difference. Lithium ions in the electrolytic medium migrate and aggregate towards the negative electrode under the action of potential difference. When discharging, the entire program is reversed. The entire working process is jointly completed by the gain and loss of lithium metal in the electrode and the migration of electrons and lithium ions in the electrolyte.
However, the chemical properties of lithium are too reactive. Lithium metal, when exposed to air, will undergo a fierce oxidation reaction with oxygen, resulting in combustion and explosion.
Therefore, in the practical application of lithium batteries, scientists make every effort to prevent the conversion of lithium ions in the electrolyte to lithium metal, and lock the metallic lithium in graphite or lithium compounds. People often hear that lithium iron phosphate and lithium cobalt oxide are materials for storing lithium atoms.
Safety issues with power batteries: Lithium ion batteries in electric vehicles do not easily self ignite
At the same time, a series of protective measures have been taken to prevent air from entering the interior of the battery. This prevents lithium metal from coming into contact with oxygen and causing an explosion.
In use, the reason why lithium batteries may self ignite is due to inadequate protective measures or serious external damage, resulting in protection failure and contact between metal lithium and air.
Common protective measures
Shell protection: In order to prevent air from entering, lithium batteries are sealed in sealed containers and usually equipped with stainless steel and aluminum alloy shells to prevent external damage. For example, Tesla's electric vehicles even use titanium alloy protective plates to prevent damage to battery containers during vehicle use, especially in traffic accidents.
Diaphragm blocking protection not only prevents external damage, but also prevents damage from inside the battery.
Usually, in order to prevent short circuits caused by direct contact between the positive and negative poles of a battery, there is a layer of separator inside the battery, which separates the positive and negative poles and allows charged ions to pass through.
However, in lithium batteries, the separator also serves another protective function. When the battery temperature is too high, the diaphragm gap will automatically close, preventing lithium ions from passing through and thus terminating the entire battery reaction. This prevents the problem of high voltage generated by the gasification of the electrolyte in the battery due to high temperature, which can damage the sealing structure of the battery.
Overcharge voltage protection not only blocks the air, but also prevents the leakage of metallic lithium from the electrode.
Scientists store and lock the metallic lithium formed during charging and discharging through the nanopores and lattice mechanisms of electrode materials.
In this way, even if the battery casing ruptures and oxygen enters, the oxygen molecules are too large to enter these small storage cells, thus avoiding the occurrence of spontaneous combustion.
However, using too high voltage or continuing to charge for too long after being fully charged can cause very dangerous damage to lithium batteries.
After the charging voltage of a lithium battery exceeds the rated voltage (usually 4.2V), if it continues to charge, the negative electrode storage cell will be filled with lithium atoms, and subsequent lithium ions will accumulate on the surface of the negative electrode material. These lithium ions undergo electron transfer due to polarization, forming metallic lithium and growing dendritic crystals from the negative electrode surface towards the direction of lithium ions.
These metal lithium without electrode protection are extremely reactive and prone to oxidation reactions and explosions. On the other hand, the formed metallic lithium crystals will penetrate the diaphragm, causing a short circuit between the positive and negative electrodes, thereby causing a short circuit and generating high temperature. At high temperatures, materials such as electrolytes will crack to produce gas, causing the battery casing or pressure valve to bulge and rupture, allowing oxygen to enter and react with lithium atoms stacked on the negative electrode surface, resulting in an explosion.
When charging lithium batteries, it is necessary to set the upper voltage limit and overcharge protection. Lithium batteries produced by legitimate battery manufacturers are equipped with such protective circuits. Automatically power off when the voltage exceeds the limit or the battery is fully charged.
Actually, spontaneous combustion is not easy
Under the heavy protection of a qualified shell, diaphragm, and circuit, spontaneous combustion of lithium batteries is not an easy task.
Especially in inorganic material lithium batteries, such as lithium iron phosphate batteries, because batteries do not use organic materials like ternary lithium batteries, even if there is material damage and short circuit inside the battery, the high temperature generated will not cause the inorganic material to decompose and produce high-pressure gas, which will then explode and self ignite. In the experiment, even if qualified lithium iron phosphate batteries are put into firewood (firewood temperature below 600 ℃), they will not explode or undergo natural conditions.
At the same time, compared to the situation where manufacturers in the early stages of the development of new energy vehicles did not fully understand the protective measures in actual vehicle use, after decades of exploration and the actual use of millions of new energy vehicles worldwide, sufficient experience has been accumulated from battery manufacturers to automobile manufacturers.
The protective strength of the shell of lithium batteries has been greatly strengthened, and even in severe traffic accidents such as vehicle disassembly, the protection of the battery can still be effective.
In the selection of battery separators, manufacturers are also fully aware of the importance of using separators with self-protection functions. At present, most high-quality lithium battery products have already used this technology. The application of electronic protection devices against overcharging has already become a mandatory standard by the country. Qualified electronic protection devices and mature battery pack management systems have greatly reduced the probability of self ignition in lithium batteries of new energy vehicles.
Based on the current cases of spontaneous combustion in new energy vehicles, none of them are caused by the battery pack's spontaneous combustion and explosion under normal driving conditions. More explosions and spontaneous combustion of lithium batteries in new energy vehicles come from extremely serious traffic accidents and improper modification of electrical equipment inside the vehicle. Under the high temperature of nearly a thousand degrees, the lithium battery was finally ignited.
For consumers, lithium batteries in new energy vehicles are generally very safe. However, it is necessary to guard against the neglect of battery protection and the hidden dangers of illegal modification of electric vehicles caused by individual manufacturers' rough manufacturing and product price wars during the outbreak of the industry.
For new energy vehicles, people always think that driving a new energy vehicle feels like carrying a time bomb, which affects the promotion and development of new energy vehicles. Actually, lithium batteries are not that scary.

Lithium ForkLift Batteries ,Ensure Quality
Our lithium battery production line has a complete and scientific quality management system
Ensure the product quality of lithium batteries

Years of experience in producing lithium forklift batteries
Focus on the production of lithium batteries

WE PROMISE TO MAKE EVERY LITHIUM BATTERY WELL
We have a comprehensive explanation of lithium batteries

QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATE
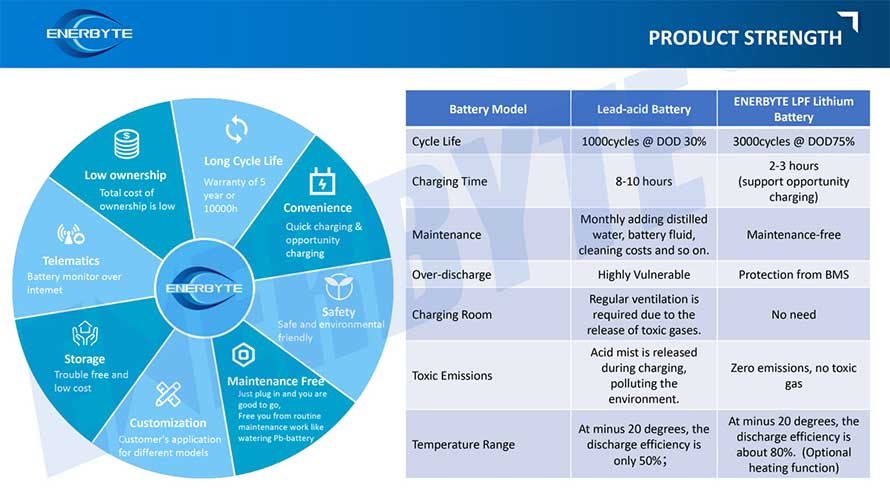
THE QUALITY OF COMPLIANCE PROVIDES GUARANTEE FOR CUSTOMERS
MULTIPLE QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATES TO ENSURE STABLE PRODUCT QUALITY
Providing customers with professional and assured products is the guarantee of our continuous progress.


Applicable brands of our products

| Linde Lithium Forklift Battery | Toyota Lithium Forklift Battery | hyster Lithium Forklift Battery |
| jung Lithium Forklift Battery | enrich Lithium Forklift Battery | hyundai Lithium Forklift Battery |
| still Lithium Forklift Battery | heli Lithium Forklift Battery | hangcha Lithium Forklift Battery |

 Service hotline
Service hotline