24-hour hotline:+8613662168047
Keyword search: battery plant , lithium battery factory , power bank works , lifepo4 battery mill , lithium forklift battery manufacturer
Due to the fact that lead-acid battery chargers are generally set in a two-stage or three-stage charging mode, the voltage levels of lithium batteries and lead-acid batteries do not match. There are also many types of lithium batteries, and their performance and protection board parameters may vary. Therefore, lithium batteries do not have a universal battery charger like lead-acid batteries. Generally speaking, lithium batteries come with a dedicated charger when they leave the factory. To protect lithium batteries, a dedicated charger is required.
The difference between lithium battery chargers and lead-acid chargers
At present, the electric vehicle chargers on the market are mainly switch mode, which have advantages such as power saving, small size, light weight, and mature technology. Freight tricycles with only lead-acid batteries also use power frequency transformer chargers, which are simple, reliable, inexpensive, and have low environmental requirements.
The switch mode power charger is essentially a voltage stabilizing power supply. Specifically, there are two types of forks: half bridge type with pulse width modulation chip TIA94 as the core and flyback type with pulse width modulation chip UC3842 as the core. The latter, due to its advantages of low cost and periodic protection, occupies over 90% of the market. The specific circuits that follow are analyzed based on these two typical circuits.
1. Lead acid charger three-stage charger
For nearly a century, the classic ordinary lead-acid charger has been charging for J2-14 hours at 0.1C, which is very beneficial for batteries. Nowadays, people's pace of life and work is accelerating, and electric vehicle chargers have been changed to 0.15C-0.2C for 6-8 hours of charging.
The so-called three stages refer to constant current, constant pressure, and eddy current. A red LED indicates a constant current or voltage stage, and a green LED indicates a trickle stage. Usually, after turning green, the battery needs to be recharged for several hours before it can truly fill up.
(1) Three important parameters of a three-stage charger
A. High constant voltage refers to the hydrogen evolution voltage of a single cell of 2.42V multiplied by the number of cells in the battery pack. The 36V charger is 2.42Vx18 cells ≈ 43.56V, and the 48V charger is 242Vx24 cells ≈ 58.08V.
A slightly higher voltage is acceptable, which is beneficial for longer constant current time and shorter charging time. A lower voltage will prolong the time it takes for the battery to be fully charged.
The three-stage charger is essentially a stabilized power supply with two output voltage values, and this signal is the high output value.
B. The low constant voltage value is 2.35V per cell chlorine evolution voltage multiplied by the number of cells in the battery pack. The 36V charger is 2.35V x 18 cells=423V, and the 48V charger is 2.35V x 24 cells=56.4V.
This voltage requirement is strict, exceeding this value will cause water loss in the electric oil: if it is too low, the battery can only eat 80-90% full. This value is the low output value of the stabilized power supply.
C. Turning current (also known as turning light current). The charger has a real-time charging current detector inside and a predetermined "turning current"
Compare the values to control the high and low output values of the regulated power supply:
When the charging current reaches this value, the control circuit will be automatically turned to output a high constant voltage value, and a red light will be set to indicate that the charging current is less than the turning current value and will be turned to output a low constant voltage value, and set to a green light.
The setting of the turning current value is related to the ampere hour of the lead-acid battery. The empirical value of around 350mA for an IOAh battery, around 500-550mA for a 17Ah battery, and so on.
This value requirement is also strict. Set a dry experience value, the battery should not be fully charged, but the time for sufficient oil will be extended; If the set value is less than the empirical value, the electric oil is prone to damage and deformation during summer. It is recommended to adjust the charger with a maximum of 50mA.
Remember: It is possible to charge a 10Ah battery with a 20Ah charger. It is not possible to charge a 20Ah battery with an IOAh charger instead!
Specialized instruments are required for measuring the three parameters. Only using a digital multimeter can test the low constant voltage value. When not connected to the battery (unloaded), use a multimeter to output a DC voltage of 200V from the gear charger, and the reading is the low constant voltage value. The high constant voltage value is generally not measurable. It can only be measured using a multimeter in the DC voltage range before the red light turns green and the battery is connected for charging.
We also need to supplement the relevant questions on the negative temperature coefficient of lead-acid batteries. For every 1 ℃ increase in temperature, the voltage at each grid end decreases by 4mV. A 48V car with 24 compartments, assuming an increase of 10 ℃ in summer, the total terminal voltage drops by approximately 1V.
If the output of the charger is still at the aforementioned stable voltage value, the battery may experience thermal runaway and dehydration. The ideal charger should have temperature compensation, but in fact, the vast majority do not.
Readers with hands-on skills can lower the voltage in summer and increase it in winter. The simplest method is to connect 1-2 6A10 diodes in series with the positive pole at the output end of the charger in the summer, and restore them to their original state in the winter.
2. Lithium battery charger
The acceptance capacity of lithium battery plates is higher than that of lead-acid batteries, and charging with IC current is also possible, which may be limited by cost and reliability. Currently, most chargers matched with 48V Hammer Turtle electric vehicles are 2A, and only chargers matched with 36V lithium electric vehicles are 5A. Based on a 10Ah battery, 5A is just 0.5c.
The charging of lithium-ion electric vehicles for users is much simpler than the charging of lithium-ion batteries, which is constant current and limited voltage charging. Voltage limit value=Single heart voltage limit value x Number of series connected electrodes. The 14 series of commonly used 48V automotive lithium-ion batteries or ternary batteries have a voltage limit of 4.2Vx14=58.8V; The 16 series of 48V automotive phosphate iron hammer cells are mostly used, with a voltage limit of 3.65VX16=58.4V. Early 36V cars mostly used 10 series of diamond acid batteries or lithium manganese batteries, with a sleep voltage of 42V x 10=42V.
Lithium ion chargers also have charging current detection and comparison circuits inside, and the charging indicator light can also change from red to green.
There is a significant difference between lithium battery chargers and lead-acid three-stage chargers:
When the charging current is greater than the set value, only the charging indicator light turns red without changing the output voltage; When the charging current is less than the set value, make the charging indicator light turn green and do not change the output voltage. That is to say, there is only one voltage before and after turning the light, which is the voltage limit value calculated earlier.
Therefore, this current setting value should be referred to as the "turning light current", which is more accurate and approximately 0.02C. The tested lithium-ion chargers provided by several manufacturers have a 10Ah lithium-ion battery pack with a lamp current of approximately 240mA to 260mA. After turning green, continue charging for a period of time before the charging current approaches zero. After the lead-acid battery turns red to green, the charging current will quickly approach zero because the high constant voltage changes to low constant voltage.
Summary: Lead acid batteries are limited by the plate's acceptance capacity, and it is reasonable to limit the charging current below 0.15C, while also taking into account the need to shorten the charging time.

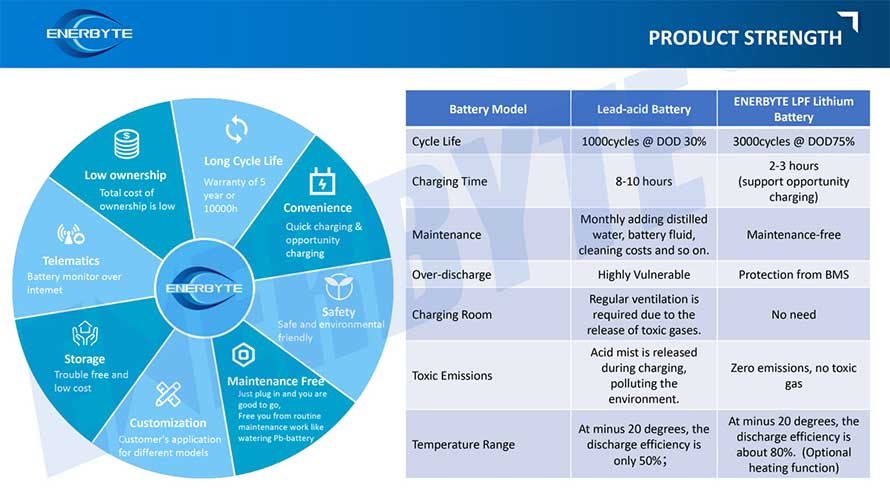
Lithium ForkLift Batteries ,Ensure Quality
Our lithium battery production line has a complete and scientific quality management system
Ensure the product quality of lithium batteries

Years of experience in producing lithium forklift batteries
Focus on the production of lithium batteries

WE PROMISE TO MAKE EVERY LITHIUM BATTERY WELL
We have a comprehensive explanation of lithium batteries

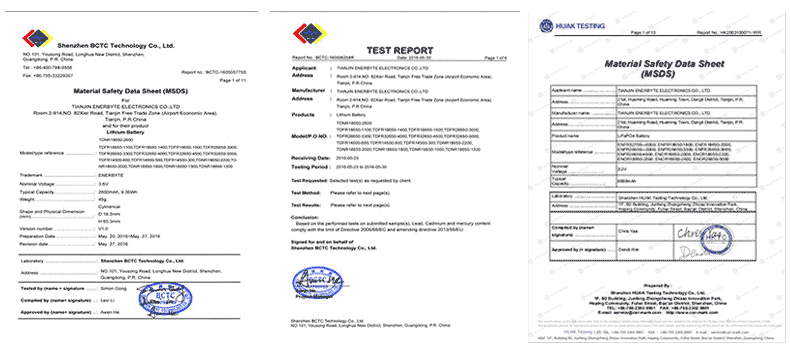
QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATE
THE QUALITY OF COMPLIANCE PROVIDES GUARANTEE FOR CUSTOMERS
MULTIPLE QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATES TO ENSURE STABLE PRODUCT QUALITY
Providing customers with professional and assured products is the guarantee of our continuous progress.


Applicable brands of our products

| Linde Lithium Forklift Battery | Toyota Lithium Forklift Battery | hyster Lithium Forklift Battery |
| jung Lithium Forklift Battery | enrich Lithium Forklift Battery | hyundai Lithium Forklift Battery |
| still Lithium Forklift Battery | heli Lithium Forklift Battery | hangcha Lithium Forklift Battery |

 Service hotline
Service hotline