24-hour hotline:+8613662168047
Keyword search: battery plant , lithium battery factory , power bank works , lifepo4 battery mill , lithium forklift battery manufacturer
Generally, 18650 lithium batteries are increased in capacity through parallel connection, for example, the 20000mah mobile power supply is usually composed of 8 2600mAh batteries or 6 3400mAh 18650 batteries. Parallel connection increases the capacity by 3.7V. Then, the voltage is increased by series connection. Two series connections result in 3.7 * 2=7.4V, and three series connections result in 12.6V and so on.
Usually, electric vehicles and laptop batteries require multiple batteries to be connected in series to increase the battery voltage to 12V or 36V48V72V, etc. If the capacity or quality of the batteries is not equal, there will always be one that consumes much during use, just like the principle of a wooden bucket's short board, where one battery or the parallel set of batteries affects the total battery voltage and capacity of the entire battery pack.
The impact is that, for example, laptops are usually 2 in parallel and 3 in series, forming batteries ranging from 10.8V to 12.6V. A set of two parallel batteries will consume first, which will cause a decrease in the capacity of the entire battery. Specifically, the battery has a short standby time, fast charging speed, and fast electricity consumption. Electric vehicles and other equipment are the same.
At this point, it is necessary to replace the battery pack to avoid the barrel effect (short board principle - the ability of a barrel to hold water depends on the shortest board of the barrel). This way, the battery can be used evenly and extended.
Measure directly with a voltmeter, if the voltage at both ends of the 18650 battery is below 2.7V or there is no voltage. Indicates that the battery or battery pack is damaged. Normal voltage: 3.0V~4.2V (Generally, 3.0V batteries will have a voltage cutoff, 4.2V batteries will have a full charge saturation, and some types may also have 4.35V)
three
If the battery voltage is lower than 2.7V, you can use a charger (4.2V) to charge the battery. After ten minutes, if the battery voltage rises, you can continue to charge until the charger prompts full charge, and then check the full charge voltage.
If the fully charged voltage is 4.2V, it indicates that the battery is normal, and it should be due to excessive power consumption during the last use, causing the battery to shut down.
If the fully charged voltage is much lower than 4.2V, it indicates that the battery is damaged. If it is a battery that has been used for a long time, it can be determined that the battery has reached its lifespan and its capacity is basically depleted. It should be replaced. There is basically no way to fix it. After all, lithium batteries have a lifespan, not unlimited.
four
If the battery is measured and there is no voltage, there are two situations. One is that the battery was originally good and stored for a long time due to low power. This type of battery has a certain chance of recovery. Generally, a lithium battery pulse activator is used to charge the battery multiple times in a short period of time. Possible repair. The general repair cost is not low, so it's better to buy a new one
Another possibility is that the battery is completely depleted, the battery separator is broken, and there is a short circuit between the positive and negative electrodes. There is no way to fix this matter. Only new ones can be purchased.
As mentioned earlier, lithium battery packs often become unusable due to one or more damaged batteries. In this case, the voltage at both ends of each battery group should be measured one by one. If there is no voltage or the voltage is significantly low (as described earlier for individual batteries), they should be removed and replaced with new batteries of the same type with similar internal resistance.
After replacement, the lithium battery pack can still be used for a similar lifespan as other batteries. This type of partial replacement generally has a lower cost. It is also a commonly used method in the current market.
three
Lithium batteries must be equipped with protective boards to limit overcharging, over discharging, short circuits, etc., which is beneficial for extending the lifespan of lithium battery packs
Lithium batteries should not be short circuited, and attention must be paid during testing
18650 lithium batteries must be equipped with protective plates for use
Lithium ion battery charging must not exceed the rated voltage and current, as well as the charging time
Lithium battery chargers need quality assurance to extend their service life
1、 Voltage related faults
1. High voltage of 12V lithium battery: After being fully charged and left idle, the battery voltage is significantly higher, while other cells are normal.
Cause of malfunction:
① Collection error;
② Poor or ineffective LMU balancing function;
③ The battery cell has a low capacity and the voltage rises rapidly during charging.
Handling method:
① The displayed voltage value of a single cell is lower than that of other cells. Measure the actual voltage value of the cell for comparison. If the actual value is higher than the displayed value and is the same as the voltage of other cells, calibrate the LMU cell voltage based on the actual value; If the measured value matches the displayed value, manually charge and balance the individual battery.
② Check if the voltage sampling line is broken or disconnected;
③ Replace LMU;
④ Replace the faulty battery pack.
2. Pressure difference: dynamic pressure difference/static pressure difference. When charging, the individual voltage quickly reaches the cut-off voltage at full charge and jumps the gun; When discharging, the individual voltage drops more rapidly than other strings; When the discharge is stopped, the individual voltage rises more rapidly than other strings.
Cause of malfunction:
① The fastening nut of the copper plate connecting the battery is loose;
② There is dirt on the connecting surface;
③ The self discharge rate of the battery cell is high;
④ The copper plate of the battery cell welding connection is open for welding (resulting in low capacity of the single unit in the string);
⑤ Individual individual cell leakage.
Handling method:
① Tighten the nuts;
② Remove foreign objects from the connection surface;
③ Charge/discharge balance for single string batteries;
④ Replace the faulty battery pack.
4. Voltage jump: When an electrical device is running or charging, the voltage of a 12V lithium battery cell jumps.
Cause of malfunction:
① The connection point of the voltage acquisition line is loose;
② LUM malfunction.
Handling method:
① Tighten the connection points;
② Replace LMU.
2、 Temperature related faults
1. Thermal management failure;
① Heating failure (heating element); When the temperature is below a certain value, heating does not turn on during charging.
Cause of malfunction:
① Heating relay or BMU malfunction;
② The heating element or relay power supply circuit is abnormal.
Handling method:
① Repair or replace fan relay or BMU malfunction;
② Check and repair the abnormal power supply circuit.
② Heat dissipation failure (fan); After the temperature exceeds a certain value, the fan does not work.
Cause of malfunction:
① Fan relay or BMU malfunction;
② The power supply circuit of the fan or relay is abnormal.
Handling method:
① Repair or replace fan relay or BMU malfunction;
② Check and repair the abnormal power supply circuit.
2. High temperature: One or several temperature points in the battery system are too high, reaching the alarm threshold during operation or charging.
Cause of malfunction:
① Temperature sensor malfunction;
② LMU malfunction;
③ Abnormal electrical connection and local heating;
④ Fan not turned on, poor heat dissipation;
⑤ Near heat sources such as motors;
⑥ Overcharging.
Handling method:
① Compare the resistance value of the temperature sensor with the displayed value. If the actual value is lower than the displayed value and is the same as other temperature values, calibrate the LMU temperature value based on the actual value;
② Tighten the electrical connection point and remove any foreign objects from the connection point;
③ Ensure that the fan is turned on;
④ Increase insulation materials to isolate from heat sources;
⑤ Suspend operations for heat dissipation; ⑥ Immediately stop charging;
⑦ Replace LMU.
3. Low temperature: One or several temperature points in the battery system are too low, reaching the alarm threshold during operation or charging.
Cause of malfunction:
① Temperature sensor malfunction;
② LMU malfunction;
③ Abnormal local heating element.
Handling method:
① Compare the resistance value of the temperature sensor with the displayed value. If the actual value is higher than the displayed value and is the same as other temperature values, calibrate the LMU temperature value based on the actual value;
② Check and repair the heating element; ③ Replace LMU.
4. Temperature difference; Refer to the high and low temperature investigation methods. Differential heating of battery cells.
3、 Charging fault
1. DC charging fault; GB/T27930-2015 Charging cannot start, charging gun jumps, SOC does not reset after charging is completed.
Cause of malfunction:
① Battery malfunction (abnormal voltage, temperature, insulation, etc.)
② BMU malfunction (abnormal charging module or charging CAN)
③ Abnormal main negative and charging relays
④ CC1 ground resistance and CC2 ground voltage abnormality
⑤ PE ground anomaly
Handling method:
① Troubleshooting battery issues
② Repair/replace failed components
③ Intercept charging messages and analyze the cause of the malfunction.
2. AC charging fault;
Cause of malfunction:
① Battery malfunction (abnormal voltage, temperature, insulation, etc.)
② BMU malfunction (abnormal charging module or charging CAN)
③ Abnormal main negative and charging relays
④ Abnormal CC to ground resistance and CP to ground voltage
⑤ PE ground anomaly
Handling method:
① Troubleshooting battery issues
② Repair/replace failed components
③ Intercept charging messages and analyze the cause of the malfunction.
4、 Insulation fault
Cause of malfunction: Water ingress into the battery box or plug-in, leakage of battery cells, high environmental humidity, insulation false alarm, and inadequate insulation of other high-voltage components (controllers, compressors, etc.) of the vehicle.
Solution: ① Positive electrode to ground. If there is voltage or insulation resistance less than the specified value, the negative electrode circuit is judged to have leakage; If there is voltage or insulation resistance less than the specified value between the negative electrode and ground, the positive electrode circuit is judged to have leakage. The leakage point can be calculated by dividing the leakage voltage by the current single string voltage value, and then analyzed and processed according to different situations.
5、 Communication failure
LUM communication failure, BMU communication failure; The whole vehicle has one or several LMU information, or the whole vehicle does not have BMS information.
Cause of malfunction:
① LMU/BMU malfunction;
② Poor contact/malfunction of LMU/BMU power supply circuit or communication line;
③ Signal interference.
Handling method:
① Replace LMU/BMU;
② Check and repair the power supply circuit/communication line;
③ Check the shielding and wiring to identify and eliminate sources of interference.
6、 SOC anomaly
1. Inaccurate;
If there is a deviation between the actual displayed value of "charged SOC" and "remaining SOC", or if the estimated actual electricity level does not correspond to SOC based on the correspondence between SOC and OCV, we believe that SOC is inaccurate.
2. No change;
Cause of malfunction:
① Communication abnormality (missing data);
② Abnormal current (Hall and its input/output circuits);
③ BMU malfunction;
④ Other battery alarms.
Processing method: ① Ensure data integrity; ② Repair/replace failed components; ③ Eliminate all battery alarms.
3. Fast decline;
Cause of malfunction:
① Abnormal communication cycle
② Abnormal current (high Hall forward current and low feedback current);
③ The individual voltage is low and drops quickly;
④ BMU malfunction;
⑤ Low temperature.
Handling method:
① Update BMU program;
② Repair/replace failed components;
4. Slow descent;
Cause of malfunction: ① Abnormal communication cycle ② Abnormal current (low Hall forward current and high feedback current) ③ BMU malfunction.
Handling method:
① Update BMU program;
② Repair/replace faulty components.
5. Jumping; Confirm if the program version number is correct
7、 Abnormal current
Cause of malfunction:
① Hall and its input and output circuits;
② Hall reverse installation;
③ When charging DC, if the BMS requires a voltage or current of 0, the charger will output at its minimum output capacity.
Handling method:
① Update BMU program;
② Repair/replace faulty components.

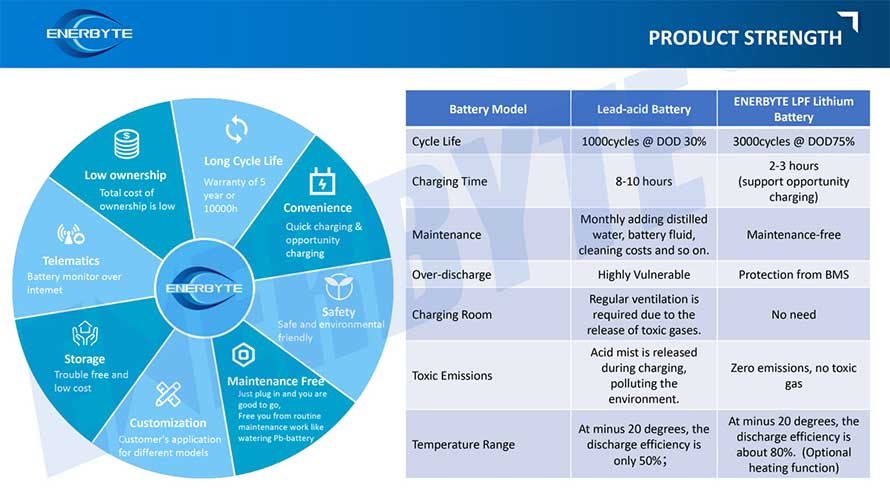
Lithium ForkLift Batteries ,Ensure Quality
Our lithium battery production line has a complete and scientific quality management system
Ensure the product quality of lithium batteries

Years of experience in producing lithium forklift batteries
Focus on the production of lithium batteries

WE PROMISE TO MAKE EVERY LITHIUM BATTERY WELL
We have a comprehensive explanation of lithium batteries

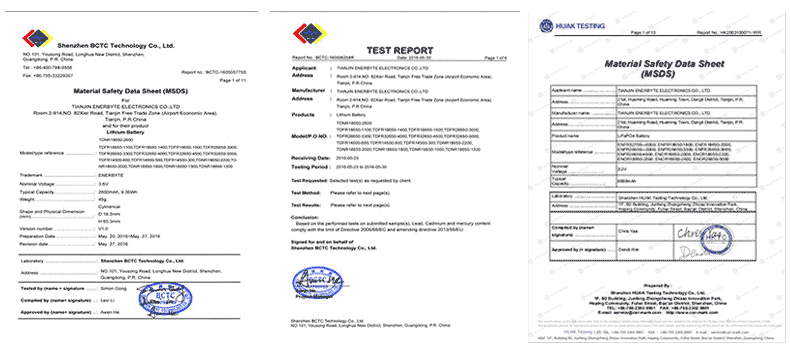
QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATE
THE QUALITY OF COMPLIANCE PROVIDES GUARANTEE FOR CUSTOMERS
MULTIPLE QUALIFICATION CERTIFICATES TO ENSURE STABLE PRODUCT QUALITY
Providing customers with professional and assured products is the guarantee of our continuous progress.


Applicable brands of our products

| Linde Lithium Forklift Battery | Toyota Lithium Forklift Battery | hyster Lithium Forklift Battery |
| jung Lithium Forklift Battery | enrich Lithium Forklift Battery | hyundai Lithium Forklift Battery |
| still Lithium Forklift Battery | heli Lithium Forklift Battery | hangcha Lithium Forklift Battery |

 Service hotline
Service hotline